
Anatomy of the hip region
bones that form joints
- ileum
- ischium
- pubic
fabrics and structures
- Ligaments and tendons surround all sides of the joint, covering and protecting the femur and its neck, as well as the glenoid socket itself.
- Cartilage covers the femoral head and part of the acetabulum.
- The subchondral area is bone tissue composed of cells and connective extracellular material.
- The joint membrane or capsule is the source of a special secretion called synovial fluid that lubricates the joint area.
- The acetabular labrum connects the acetabular rim to the transverse ligament.
anatomical structures located next to the hip joint
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue - the outer shell of the body
- The muscles of the thighs, pelvis, lower back, and hips provide joint flexibility and strengthen it from the outside
- Extra-articular ligaments - perform strengthening functions and are located around the joint capsule
- Periarticular bursae are bundles of connective tissue that prevent friction between soft and hard tissue
risk factors
- leather
- muscle
- Ligaments (extra-articular, femoral head)
- periarticular bursa
- TBS capsules
- cartilage
- acetabular labrum
- subchondral area
- immune system diseases
- Joint damage caused by excessive physical activity
- elderly
- Metabolic disorders
- other illnesses
characteristics of pain
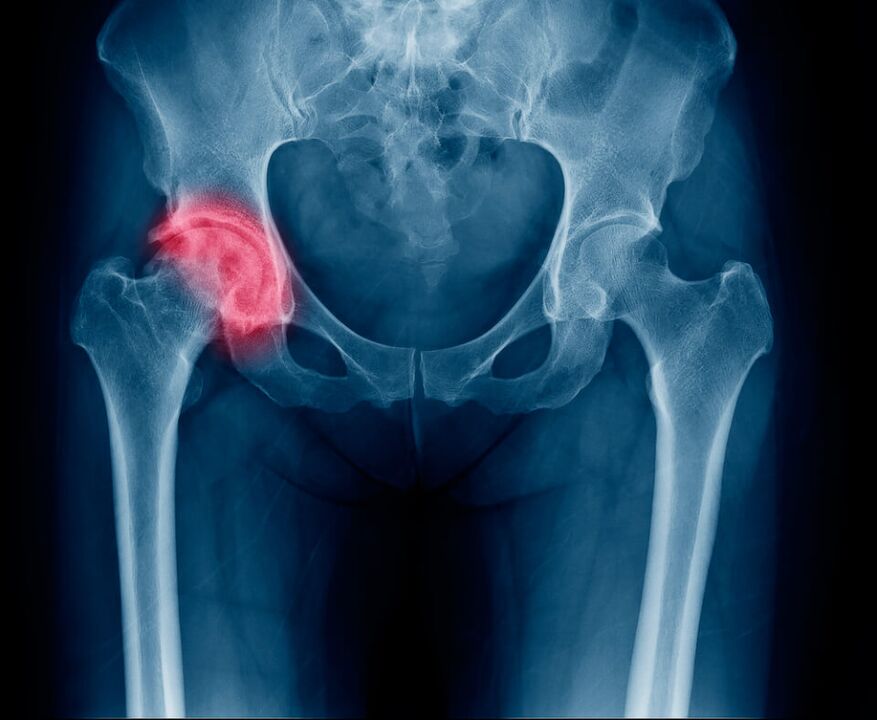
Hip pain that radiates to the leg
- joint tumors
- Infectious arthritis - occurs due to pathogenic damage
- Fractured femur (head or neck)
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes Pathology - Femoral head cartilage necrosis
- Juvenile epiphysis - structural destruction and inflammation of the joint head
pain when walking
- Discomfort that occurs when starting to walk and gradually subsides - a sign of inflammation of the periarticular bursae
- Discomfort that gradually increases from the moment you start walking - Inflammation of the articular surface of the hip joint
- Persistent, high-intensity pain with impaired joint function - occurs with dislocations and fractures
- Pain that occurs towards the end of the night - the result of deformation of the cartilage of the femoral head and (or) acetabulum, which rub against each other and become inflamed
- Moderate pain is a sign of minor injuries and bruises
Pain when abducting the leg
reason
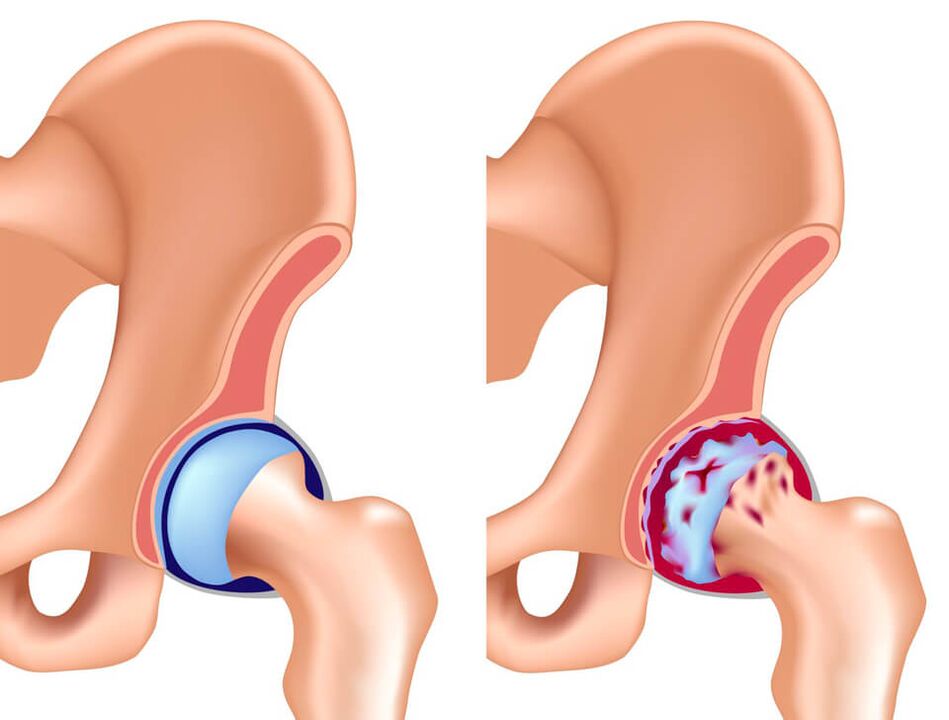
- arthritis
- Hip arthrosis
- Trochanteric bursitis
- Tendinitis
- infectious pathology
- hereditary disease
- Tumor formation in the pelvic area
arthritis
- temperature rise
- pain and swelling in the joint area
- Movement disorders
Hip arthrosis
Trochanteric bursitis
Tendinitis
- Thyroid pathology
- Metabolic disorders
- arthritis
- joint
- Inflammatory process of systemic or infectious origin
- hip dysplasia
Infect
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is a disruption of the blood supply to the groin area, causing tissue death. The pain associated with this disease is acute and severe. This problem is more common in men.
- Septic arthritis is a serious condition that requires immediate treatment. If medical help is not sought promptly, sepsis may occur. Associated symptoms are systemic intoxication, pain and swelling in the affected joint areas, and difficulty with motor activities.
- Tuberculous arthritis is common in children and is characterized by a slow progression. Associated symptoms include increased fatigue, reduced motor activity, and muscle atrophy. When a purulent abscess develops, varying degrees of pain may intensify.
hereditary disease
Bone and soft tissue tumors
- Lipoma
- rhabdomyomas
- Fibroma
- Hemangioma
- Neuroma
what to do
- lung- Bruising after an injury. A cold compress should be applied to the painful area to reduce swelling. To reduce pain, it is recommended to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is recommended to consult a doctor.
- ease- Usually occurs in disorders of the hip joint, with difficulty in motor activities and an increase in body temperature. Discomfort can increase during physical activity. It is necessary to consult a rheumatologist.
- strong- Occurs due to dislocations and fractures. accompanied by limitation or inability to perform physical activities. If you are experiencing severe hip pain as a result of an injury, you should contact an ambulance.
Which doctor should I contact?
- traumatologist— Hip pain due to physical activity, sprains, falls, and other injuries
- rheumatologist- Sudden onset of joint pain for no apparent reason
diagnosis
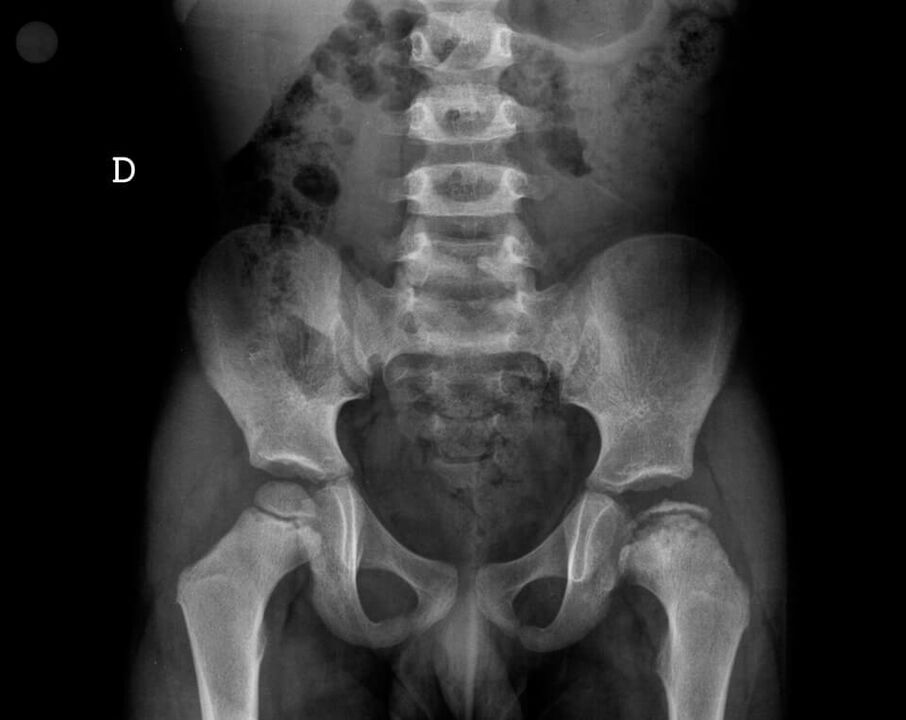
- radiography- Use X-rays to examine specific areas of the body
- CT and MRI- Modern and accurate diagnostic methods that allow you to obtain information-rich images of the joint and its surrounding areas
- Microbiological examination of biological material samplesAllows detection of the presence of pathogenic microorganisms: viruses and bacteria
- immune blood test- Allows you to identify immune diseases and determine the presence of certain autoantibodies
- Arthroscopy (endoscopy)— Examination using a probe allows samples of joint tissue to be collected for further study
- Laboratory tests for effusion- Collect intra-articular fluid samples during puncture to identify the pathogens of infectious diseases and check for sterility
treat

drug
- NSAIDs- Helps reduce pain and relieve swelling
- Means to improve microcirculation- Helps restore blood circulation and nutrition to joint tissues
- chondroprotectant- Promote the repair of cartilage tissue
- muscle relaxants- Reduce pain and improve blood flow to damaged areas
- Hormone drugs- Relieves pain and suppresses inflammation
surgical
prevention
- take a walk often
- physiotherapy
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E

















































